Table of Contents
What is environmental sustainability and how can it be achieved?

Environmental sustainability refers to the responsible management of natural resources to ensure that they remain available for future generations, while maintaining ecological balance. As the world grapples with climate change, deforestation, and pollution, sustainable practices have become crucial for nations like India. Achieving sustainability requires collaborative efforts across society, including the government, businesses, and individuals.
Strategies to achieve environmental sustainability in India?
India, being one of the fastest-growing economies, faces unique challenges in achieving environmental sustainability. Its diverse ecosystems, large population, and rapid urbanisation require innovative approaches to ensure the country’s resources are managed responsibly. Sustainability in India can be achieved by focusing on key areas like renewable energy, sustainable agriculture, waste management, and biodiversity conservation.
- Transitioning to renewable energy sources
India’s growing demand for energy is primarily met through fossil fuels, which contribute significantly to greenhouse gas emissions. To address this, transitioning to renewable energy sources is essential. Renewable energy, such as solar, wind, and hydropower, offers a cleaner alternative that reduces dependency on coal and oil, helping the country lower its carbon footprint.
By investing in renewable energy, India can ensure a sustainable and secure energy future.
| One of the most significant examples of this effort is the Pavagada Solar Park in Karnataka, the world’s largest solar park, which spans over 13,000 acres. This project demonstrates India’s commitment to reducing its carbon emissions while meeting its growing energy needs sustainably. |
- Promoting sustainable agriculture
Agriculture plays a crucial role in India’s economy, supporting livelihoods and ensuring food security. However, conventional agricultural practices often lead to land degradation, water scarcity, and excessive use of chemical fertilisers, which negatively impact the environment. Sustainable agriculture promotes methods that reduce environmental harm while maintaining or even improving productivity.
By adopting eco-friendly practices such as organic farming, crop rotation, and water-efficient irrigation, India can move toward more sustainable agricultural systems.
| Example – is Sikkim, which became the first organic state in India. The state’s focus on organic farming has not only preserved the environment but has also improved soil health and water conservation, showcasing how sustainability can be achieved in agriculture. |
- The circular economy in India
The traditional linear economy of “take, make, dispose” results in significant waste and resource depletion. In contrast, a circular economy aims to keep products, components, and materials in use for as long as possible, promoting reuse, repair, and recycling. This model helps reduce pressure on natural resources while also creating economic opportunities.
India has begun to embrace the circular economy, especially in managing electronic waste (e-waste). E-waste, if not handled properly, can release toxic substances into the environment.
| Example – Companies like Attero are pioneering e-waste recycling in India, providing a sustainable solution to this growing problem. By recycling and refurbishing electronics, Attero contributes to reducing waste and conserving resources, exemplifying how the circular economy can be implemented in India. |
- Conservation of ecosystems and biodiversity
India is home to a diverse range of ecosystems, from the Himalayan mountains to the Western Ghats and the Sundarbans mangroves. These ecosystems support a wide variety of plant and animal species, making biodiversity conservation critical for maintaining ecological balance. Unfortunately, deforestation, habitat loss, and illegal wildlife trade threaten many of these species.
Conserving ecosystems is essential not only for preserving biodiversity but also for maintaining the natural resources that humans rely on, such as clean air, water, and fertile soil.
| Example – India’s Project Tiger and Project Elephant are successful initiatives aimed at protecting endangered species and their habitats. Additionally, the Green India Mission, which focuses on reforestation and increasing forest cover, helps combat climate change and restore degraded ecosystems. |
By prioritising these key areas—renewable energy, sustainable agriculture, a circular economy, and ecosystem conservation—India can work towards achieving environmental sustainability. Each of these strategies addresses critical environmental issues while also promoting long-term economic and social benefits for the country.
What is the role of qualified policymakers in achieving environmental sustainability?
While localised initiatives play an important role, large-scale environmental sustainability requires well-formulated national policies. Having highly qualified and experienced policymakers at the helm is crucial for integrating sustainability into India’s development agenda.
For example, India’s National Action Plan on Climate Change (NAPCC) is a comprehensive policy framework aimed at addressing climate challenges through eight national missions, ranging from solar energy to sustainable agriculture. Expert policymakers in India are instrumental in crafting these policies that balance the country’s developmental needs with environmental protection.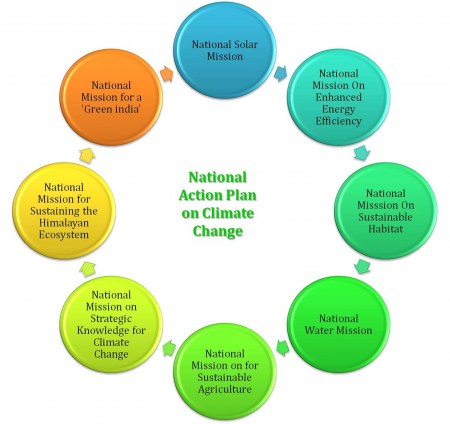 Source – https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEilN09uftCqEtM0hYrsmZ1sNdFjioTZhghH81IaNTBX1XtoeteVXh1j8lKeAhrd8-D7D8Em1r_C_FhiRUyw0Vr9n6bpaVK0r3Dd8DByiIPmNBQLEp4-rjVKe81zj4KwepItvlNluRje-EP_/s640/NAPCC.jpg One of the most notable initiatives is the Swachh Bharat Mission, which was launched with the goal of making India free of open defecation and improving waste management. |
Policymakers with a deep understanding of environmental issues, social impact, and economics are better equipped to design regulations that drive sustainability while promoting economic growth. In India, policymakers are increasingly focusing on creating a green economy that supports the environment without compromising development.
Are you an aspiring policymaker?
Public policy aspirants who wish to make a significant difference in environmental sustainability must acquire the right education and skills. Formal education in public policy equips future leaders with the knowledge and tools to tackle complex challenges, such as climate change, pollution, and resource management, on a large scale.
The Indian School of Public Policy (ISPP) offers a flagship Post Graduate Programme in Public Policy, Design & Management, which provides an in-depth understanding of public policy formulation.
It prepares students to think critically, design impactful policies, and manage their implementation efficiently. The curriculum integrates classroom learning with real-world applications, leadership training, and systems thinking, which are essential for developing the next generation of policy executives.
This programme offers aspiring policymakers the opportunity to work on pressing issues such as environmental sustainability, ensuring they are well-equipped to drive positive change in India and beyond.
Check out ISPP’s PDM curriculum.
Conclusion
Achieving environmental sustainability in India is a multifaceted challenge that requires the collective effort of individuals, businesses, and governments. Whether through renewable energy, sustainable agriculture, a circular economy, or conservation initiatives, India is taking meaningful steps toward sustainability. However, systemic change can only be realised through the work of well-qualified policymakers who design and implement effective policies.
For those aspiring to join this crucial sector, formal education in public policy from a leading institution like ISPP offers the knowledge and skills needed to influence environmental policies and contribute to a sustainable future.
Register your Interest to Study at ISPP
FAQS
Infographic: