The Formulation And Development of Public Policies In India
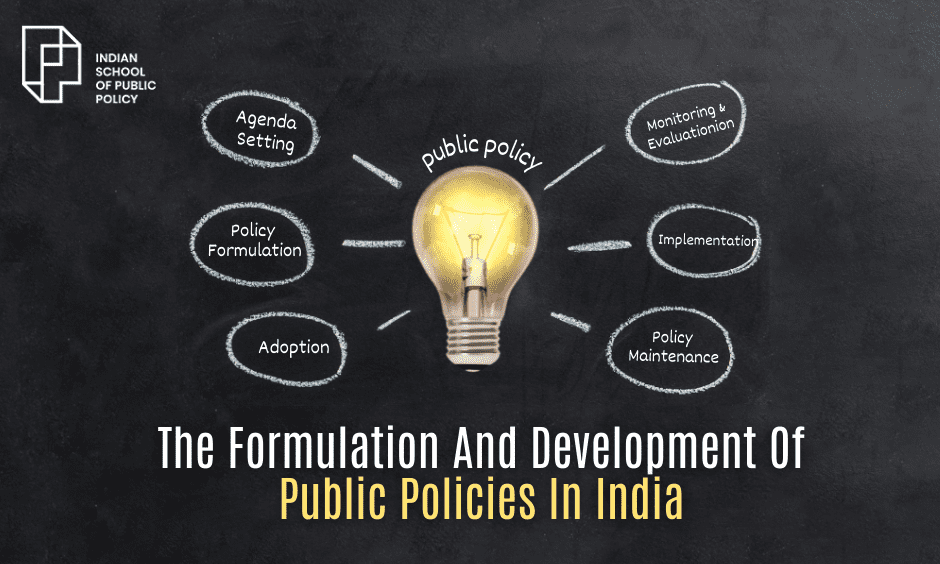
Public policy is a set of laws, regulations, directives, and budget allocations that governments or their representatives put in place to achieve public good goals. This process is an iterative one, with many players involved, leading to a policy determined by various interests and options. This also means that government policies are continually changing. As governments assess who benefits from or is affected by the policies they make, they often review and revise them to keep up with the times. For instance, India recently released an updated version of its New Education Policy (NEP) in 2020. This included new elements like guidance on using ed-tech in the classroom, replacing the NEP that had been instituted in 1986. The policy-making process is an ideal framework for developing, executing, and assessing the effectiveness of policies. It usually consists of six steps: agenda setting, policy formulation, adoption, implementation, evaluation, and policy maintenance.
The policy-making process is an iterative one, with many players involved, leading to a policy determined by various interests and options.
The Stages of A Policy Cycle
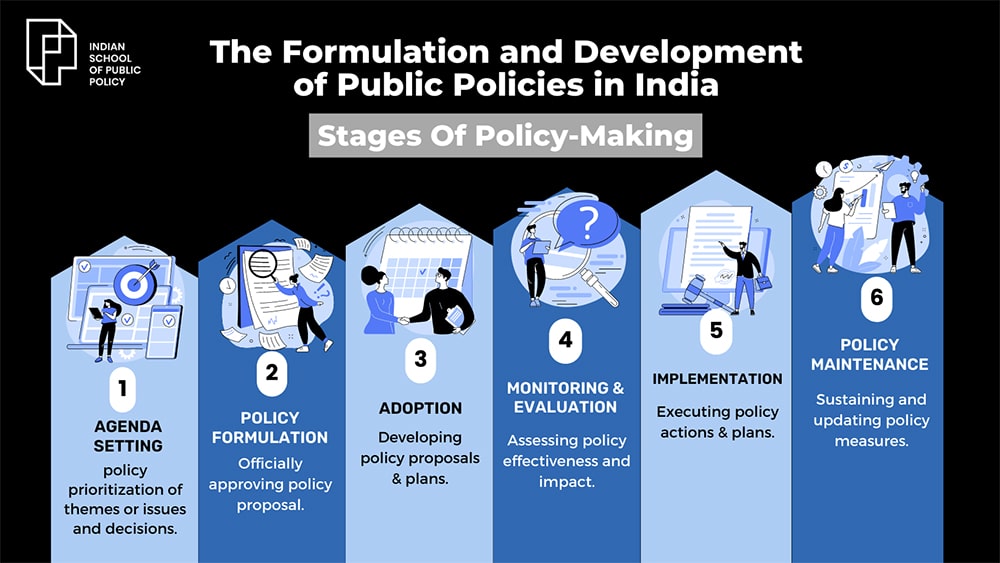
Agenda Setting – In this stage, the need for government intervention is revealed to decision-makers, with particular matters being looked into and the most pressing being prioritised. Examining these issues is crucial in deciding what the policy should look like.
For example – Beti Bachao, Beti Padhao campaign launched in 2015 was aimed at setting the agenda for improving the declining child sex ratio in India. The campaign aims to create awareness and sensitize communities about the importance of educating and empowering girls. The campaign is focused on creating a gender-favorable environment that promotes the education and protection of girl children.
The interpretation of what constitutes a problem is often debatable and relies on the existing government’s ideologies, outlook towards benefits, and bias. The NITI Ayog plays an integral role in this phase.
Policy Formulation – This is the stage that sets up the policy. Objectives are determined, costs are calculated, policy instruments are selected, potential impacts are analyzed, and stakeholders are identified. Several solutions can be proposed while aiming to meet goals under existing bounds.
For example – Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana – The Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana is a crop insurance scheme launched by the Indian government in 2016. The scheme aims to provide financial support to farmers in the event of crop failure due to natural calamities, pests, or diseases. The policy was formulated to mitigate the risks faced by farmers and to encourage them to adopt modern agricultural practices.
Usually, public policies are created without consulting sources external to the government, or critically analyzing the issues involved. Before turning the proposals into official policies, more comprehensive analyses should be conducted such as cost-benefit analysis, economic forecasting, operations research and systems analysis, and budgeting analysis with current information. It is also beneficial to gauge the opinion of those people who will be affected by the policy because it can affect the success of the policy.
Adoption or Legitimation – This is a critical stage in the decision-making process, involving two institutions – the executive and the legislature or Parliament.
- The Executive – The real executive which includes the Council of Ministers and Prime Minister’s Office considers the policy and then presents it before the Parliament.
- The Parliament – Parliament is the highest body when it comes to making public policies in India. It reigns supreme since the Council of Ministers headed by the PM is held accountable to Parliament. Therefore, its role takes on more of a “constitutional procedural device” for validating public policy by passing bills through a majority vote from the members present.
Implementation – Once the bill is signed into law by the President, the next step is to figure out how to put it into action. This typically involves setting up a structure that connects those in the field so that they can implement the policy at the ground zero level.
For Example – Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MGNREGA) – The MGNREGA is a social security measure that guarantees 100 days of wage employment to every household in rural areas of India. The policy was implemented in 2006 and has been successful in providing employment opportunities to millions of people in rural India.
Evaluation – In this stage the government assesses the effectiveness of the policy they have implemented, to determine if it has been implemented correctly and has had the desired impact. As there may be various ways to measure the results, it can lead to varying evaluations of the effectiveness, depending on the standards of measurement leveraged.
For Example – Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY) – PMJDY was launched in 2014 to provide financial inclusion to every household in India. The policy was evaluated to assess its effectiveness in achieving its objectives and making changes to improve its implementation.
For the government to keep tabs on all its programs and initiatives, NITIAayog is continually monitoring and evaluating their implementation.
Policy Maintenance, Succession, or Termination – This determines whether or not, the policy will be maintained by improving or building upon it. Usually, if there are issues with the existing policies, they can be adjusted or ended.
For Example – National Commission for Backward Classes – The National Commission for Backward Classes was set up in 1993 to investigate and recommend measures for the welfare of backward classes in India. The commission was terminated in 2018, and a new commission, the National Commission for Socially and Educationally Backward Classes, was set up in its place. This decision was made to expand the scope of the commission and address the needs of other socially and educationally backward classes in India.
In the policy-making process in India, the role of the Judiciary cannot be ignored. The Constitution of India issues the Judicial Review – the authority to check the constitutionality of government policy actions. Hence, the Judiciary plays a constructive role in promising judicial scrutiny in policy formulation in India.
The policy-making process in India consists of six steps: agenda setting, policy formulation, adoption, implementation, evaluation, and policy maintenance. The role of the Judiciary is also crucial and cannot be ignored.
Register your Interest to Study at ISPP
Contribution Of ISPP
Founded in 2019 by India’s leading public policy think tank – Centre for Civil Society (CCS), the Indian School of Public Policy has been created with the help of renowned policymakers, experts, and influencers. Committed to offering world-class faculty, extensive industry connections, and an innovative approach to policy design and management, ISPP is dedicated to revolutionizing the art of policymaking.
The ISPP’s flagship programme – Post Graduate Program in Public Policy, Design, and Management is the perfect choice for citizens looking to have an impact on public policy. The comprehensive one-year course contains seven terms of seven weeks each that guides students as they learn the science of policymaking.
This program provides an extensive comprehension of public policies and equips students with the knowledge and skills to become better policy analysts and executives. During the tenure of the course, the students will develop an understanding of public policy, financial concerns and operations, ethical considerations, and how to develop and implement successful practices across public administration and policy, the key focus areas of the programme pedagogy.
Founded in 2019 by India’s leading public policy think tank – Centre for Civil Society (CCS), the Indian School of Public Policy’s flagship programme is for citizens interested in making an impact in the public policy sphere.
FAQs
What is the role of the Judiciary in policy-making in India?
In the policy-making process in India, the role of the Judiciary cannot be ignored. The Constitution of India issues the Judicial Review – the authority to check the constitutionality of government policy actions. Hence, the Judiciary plays a constructive role in promising judicial scrutiny in policy formulation in India.
What is the role of parliament in the policy-making process in India?
Parliament is the highest body when it comes to making public policies in India. It reigns supreme since the Council of Ministers headed by the PM is held accountable to Parliament. Therefore, its role takes on more of a “constitutional procedural device” for validating public policy by passing bills through a majority vote from the members present.
What happens in the evaluation stage of the policy-making process in India?
In the policy-making stage, the government assesses the effectiveness of the policy they have implemented, to determine if it has been implemented correctly and has had the desired impact. As there may be various ways to measure the results, it can lead to varying evaluations of the effectiveness, depending on the standards of measurement leveraged. For the government to keep tabs on all its programs and initiatives, NITIAayog is continually monitoring and evaluating their implementation.
What is the importance of public policy?
Public demands, combined with the increasing complexity of social issues, mean the results of poorly designed and implemented public policies could be devastating. Moreover, public policies usually outlast governments and politicians long after they are out of power, so it is important to support policy advocates that you believe in.
How is ISPP contributing to the Public policy domain?
Founded in 2019 by India’s leading public policy think tank – Centre for Civil Society (CCS), the Indian School of Public Policy’s flagship programme is for citizens interested in making an impact in the public policy sphere. This program provides an extensive comprehension of public policies and equips students with the knowledge and skills to become better policy analysts and executives. During the tenure of the course, the students will develop an understanding of public policy, financial concerns and operations, ethical considerations, and how to develop and implement successful practices across public administration and policy, the key focus areas of the programme pedagogy.