How policies shape bureaucratic structures and decisions

Policies and their role in shaping bureaucratic structures and decisions in India
Have you ever wondered how massive schemes like Ayushman Bharat or MGNREGA reach millions of people across India? Who ensures that every child receives free education or that urban infrastructure projects get implemented efficiently? These functions are carried out by India’s bureaucracy, but the blueprint guiding them comes from certain regulations. These regulations form the backbone of governance, providing a clear framework for action. Without it, bureaucratic decisions would be scattered, inefficient, and often ineffective.
Let’s understand how policies shape the structure and decision-making of India’s bureaucracy.
How does Public Policy shape bureaucratic structures?
The Public Policy, which is a fundamental framework model that ensures the total functionality of governance systems, describes and implements the functioning of governance systems. According to policy, which involves various layers of officials and institutions and with no clear organisational framework, there may easily be chaos and inefficiency. The decision-makers establish coherent systems that work well, with clear roles, hierarchies, and mechanisms of accountability, thus, allow governments to meet their goals by delivering them successfully.
Public Policy is a model for the arrangement of interactions that take place between the different administrative layers, thus, performing common tasks. Public Policy makes it possible to run organisations more efficiently by defining responsibilities, setting up a chain of command, and integrating transparent systems.
1. Defining roles and responsibilities
Public Policy is responsible for the absence of vague notions in the administration by assigning clear responsibilities to different bureaucratic stakeholders. As a rule, the individual function is always an essential point in the scheming of the proper official or department, thus ensuring the non-occurrence of double locations and extra activities.
| Example: The National Rural Health Mission (NRHM) allocates duties like health notification, vaccination campaigns, and the addresses of patients to the different levels of workers in the healthcare sector, including district health officers, doctors, and ASHAs. This coherency facilitates the optimal allocation of resources and, therefore, the better provision of rural healthcare services. |
2. Creating hierarchies and chains of command
To have a smooth functioning body, the decisions should easily flow across administrative levels. However, Public Policy is the key to the hierarchies that are built and it makes up the organisation with top authorities, middle managers, and field-level administrators.
| Example: The Food Security Act, 2013 is a combination of central ministries in charge of the funds, state governments, and local bodies that identify the beneficiaries. This flow of the order of responsibility ensures food to reach the destination where it is aimed at arriving well without too much hold-up. |
3. Institutionalising transparency and accountability
They are validating Public Policy in the context of the monitoring and evaluation of the implementation. This is done through the use of the devices that control the performance and outline the healthily running Demos.
| Example: The RTI act 2005 allows the citizens to demand information about the government projects which they are interested in. This has created a public space of accountability where the officials are forced to deal in line with the principles of transparency and integrity. |
India’s bureaucratic structure and the decision making process
The Indian bureaucracy is organised in a hierarchical manner and operates at three levels of governance:
central, state, and district:
➤Central level
The Indian Administrative Service (IAS), comprising the highest-ranking civil servants, is tasked with formulating and implementing policies at both central and state levels. Other key services at this level include the Indian Police Service (IPS), responsible for law enforcement, and the Indian Foreign Service (IFS), which manages diplomatic relations.
➤State level
At the state level, officers handle state-specific administrative duties and ensure the implementation of central government policies at the grassroots level, aligning them with local needs.
➤District level
District-level administration is overseen by district officers, predominantly IAS officers, who are responsible for governance, maintaining law and order, and ensuring the effective execution of government policies.
How does Public Policy influence bureaucratic decisions?
Public Policy is the guidebook for decision-making that is used by bureaucrats. This makes it easy for them to prioritise their task of goal distribution and make justified choices based on data. When we look at a country with such diversity as India, we can see that there are pressures on different parts and areas of the country. When policies are not clear enough, it is easy for the leaders to make decisions on a random basis or compromise on the right path. Public Policy is the tool that ensures the fact that our decisions are logical, and at the same time, they are in the national interest and are based on evidence-based practices.
Bureaucrats, who are most often seen as the executors of government policies, use Public Policy as a framework through which they make decisions and take actions. Policymakers offer a structured framework to the bureaucrat that will help them address the pressing issues more systematically, be it through crisis management or developmental projects.
1. Setting priorities
Public Policy is a procedure used by bureaucrats to recognise the neediest requirements of society and then distribute the allocable resources as per their importance. Prioritising key areas make public policies concentrate their attention on tasks with the highest potential.
| Example: Throughout the COVID-19 pandemic outbreak, Public Policy was aimed at vaccine procurement, setting up healthcare infrastructure, and delivering relief packages to the most affected communities – The prioritisation was incredibly successful as it allowed for the saving of numerous lives while helping to revive the economy. |
2. Providing frameworks for decision-making
Lacking standard guidelines, bureaucratic decisions could differ dramatically leading to the waste of resources. Public Policy is a comprehensive framework for decision-making, which warrants that every decision is in line with the government’s goals.
| Example: The Make in India initiative is meant to boost domestic industry and attract foreign direct investments. Authorities refer to the guidance to select projects, which would become incentives and approvals, amid the regime’s economic motivation to enable a business-friendly climate. |
3. Encouraging evidence-based governance
Public Policy ensures the use of research, data, and analytics in decision-making. This method guarantees that governance is always based on facts, which helps in minimising the chances of any decision-making being arbitrary or subjective.
| Example: For instance, the Aspirational Districts Programme is an initiative that identifies districts lagging behind in important developmental indexes. The administration of the data enables them to use the available funds efficiently, monitor the process closely, and rework the strategies if required on time. |
Examples of impactful Public Policies
Green revolution Punjab spearheaded India’s Green Revolution, gaining recognition as the nation’s “granary” and playing a pivotal role in transforming agricultural productivity. | The Green Revolution in the 1960s was a transformative Public Policy initiative that addressed India’s food security challenges. At the time, India faced frequent famines and relied heavily on food imports. Policymakers introduced high-yield variety (HYV) seeds, chemical fertilisers, and improved irrigation techniques to revolutionise agriculture. Bureaucrats played a pivotal role in implementing these policies, from educating farmers to distributing resources. As a result, India became self-sufficient in food production, significantly reducing its dependency on imports. |
| The Aadhaar policy introduced a 12-digit unique identification system, making governance more efficient and transparent. It streamlined welfare schemes by eliminating duplicate or fake beneficiaries, ensuring that subsidies and benefits reached the right individuals. For instance, under the Aadhaar-enabled Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT) system, subsidies for LPG gas cylinders are directly credited to eligible beneficiaries, reducing corruption and leakages. Policymakers and bureaucrats collaborated to build this robust system, which now underpins numerous government initiatives. | Aadhaar Source – https://www.squareyards.com/blog/aadhaar-card-centers-in-mumbai-aadhpan |
GST implementation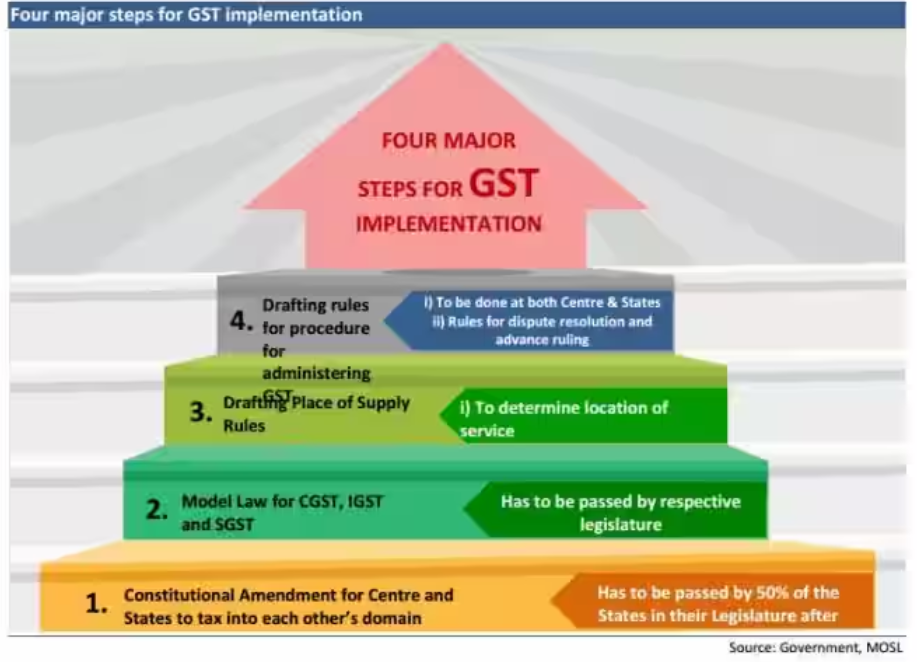 Source – https://cdn.zeebiz.com/sites/default/files/styles/zeebiz_850x478/public/2016/08/02/4988-table2.jpg?itok=1XzFULAH | The Goods and Services Tax (GST) policy unified India’s fragmented indirect tax structure into a single tax system. Policymakers designed the GST to simplify taxation, improve compliance, and promote ease of doing business. Bureaucrats across states worked tirelessly to implement this policy, conducting workshops for businesses, resolving technical glitches, and ensuring a smooth transition. Today, GST is a cornerstone of India’s tax reforms, reflecting the power of well-crafted and well-executed Public Policy. |
What’s in it for the budding policymakers?
Public Policy isn’t just about creating rules; it’s about shaping a nation’s future. Aspiring policymakers have the opportunity to design frameworks that uplift millions. Leading Public Policy institutes offer holistic programmes like Post Graduate programme in Public Policy, Design & Management that equip students with the skills to analyse challenges, design impactful policies, and drive positive change in society.
By studying Public Policy, you can contribute to building a more equitable and efficient India.
The synergy between Public Policy and bureaucracy
India’s bureaucracy, vast and complex, thrives on the clarity and direction provided by Public Policy. From structuring roles to guiding decisions, policies ensure that governance remains efficient, transparent, and citizen-centric. For aspiring Public Policy professionals, this field offers a chance to create meaningful frameworks that solve real-world problems and shape India’s future.
Register your Interest to Study at ISPP
FAQS
What is the role of Public Policy in governance?
Public Policy acts as a roadmap for governments and bureaucrats, outlining objectives, strategies, and processes to address societal challenges.
How does Public Policy influence bureaucratic decisions?
Public Policy provides frameworks, sets priorities, and promotes data-driven governance, ensuring that decisions align with national goals.
What is an example of Public Policy shaping bureaucracy?
The Food Security Act established a multi-level structure for food distribution, defining roles and responsibilities across central, state, and local governments.
What skills do you need to become a policymaker?
Analytical thinking, problem-solving, ethical reasoning, and knowledge of governance are essential for designing effective policies.
Why is Public Policy a critical field for aspirants?
Public Policy allows individuals to design solutions for pressing challenges, shaping the nation’s development and creating meaningful impact.