Analysing The Impact Of India’s Fiscal Policy On Economic Growth
India holds the position of being the world’s seventh-largest economy in terms of GDP and the third-largest when measured by PPP. The short-term growth outlook remains promising. The International Monetary Fund has hailed the Indian economy as a “bright spot” on the global stage. In a significant achievement, India topped the World Bank’s growth outlook for 2015-2016, marking a notable growth rate of 7.6%, with expectations of further growth at 8% in the coming years. Economic growth revolves around the management of public funds, encompassing revenue generation and expenditure allocation. In the pursuit of generating revenue and directing government spending, a strategic framework referred to as budgetary policy or fiscal policy is crafted by the government. This policy delineates the financial actions taken to sustain public finances.
Let’s understand
What Is Fiscal Policy?
Fiscal policy plays a pivotal role in the government’s financial operations, focusing primarily on revenue generation through taxation. It exerts a direct impact on the financial resources available to the public. In economic terms, fiscal policy entails the government’s strategic use of revenue collection and spending to shape the economic landscape. This influence becomes apparent when the government modifies taxation levels and expenditure patterns.
The primary challenge faced by governments in many developing countries lies in balancing their infrastructure and social investment needs while ensuring fiscal responsibility. This blog delves into the impact of fiscal policy on the dynamic economic landscape.
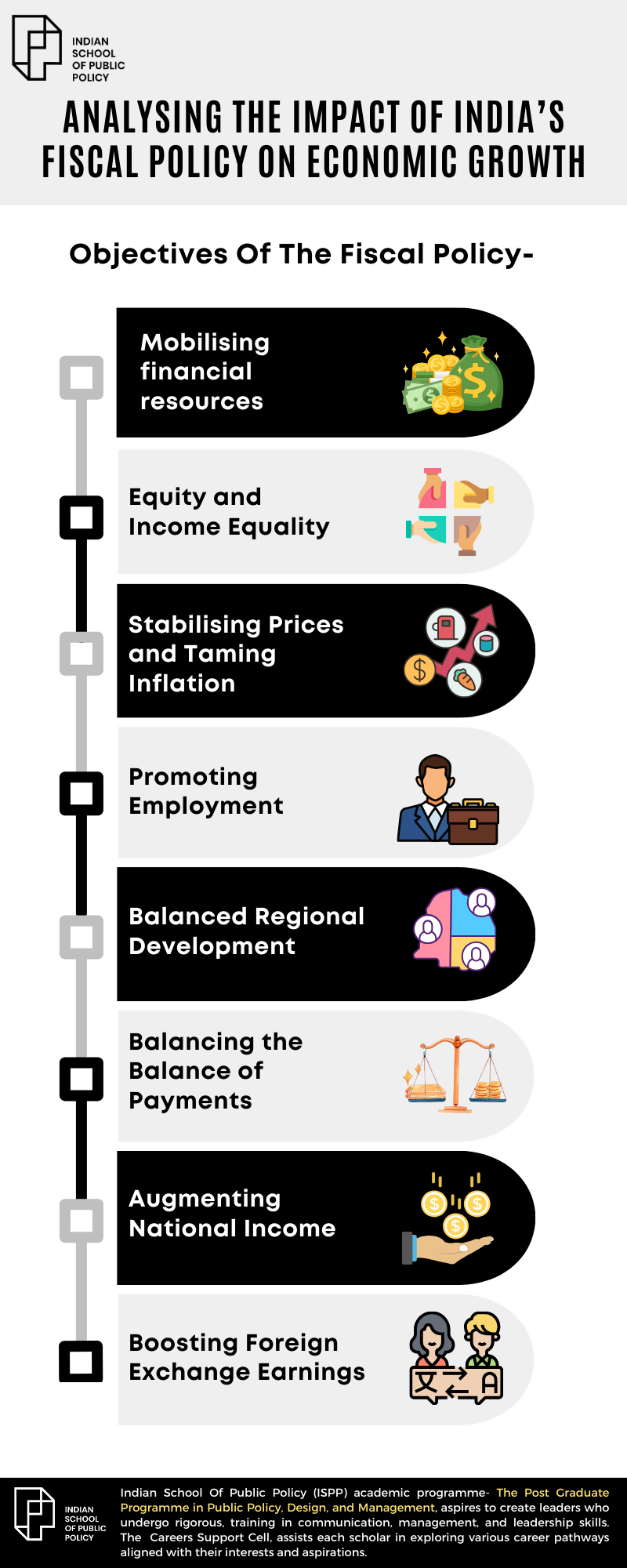
What Are The Objectives Of The Fiscal Policy?
Resource Mobilisation for Rapid Development
Fiscal policy aims to ensure swift economic growth and development, a goal achieved through effective resource mobilisation. In India, the central and state governments leverage fiscal policies to attain this objective.
Mobilising Financial Resources Involves
- Taxation: By employing sound fiscal policies, the government mobilises resources via both direct and indirect taxes, making taxation the cornerstone of resource collection in India.
- Public Savings: Resource accrual is facilitated through public savings, achieved by curbing government expenditure and bolstering surpluses in the public sector.
- Private Savings: Through judicious fiscal measures, such as tax incentives, the government can raise resources from the private sector and households. Moreover, resources can be mobilised via government borrowings, encompassing treasury bills, the issuance of government bonds, loans from domestic and foreign entities, and deficit financing.
Equity and Income Equality
Fiscal policy is harnessed to foster equity and social justice by narrowing income disparities among distinct societal segments. Direct taxes, particularly income tax, impose higher burdens on the affluent in contrast to lower-income groups. Similarly, indirect taxes exact greater tolls on semi-luxury and luxury items, predominantly consumed by the upper middle class and the wealthy. The government dedicates a significant portion of its tax revenue to implementing Poverty Alleviation Programmes aimed at enhancing the circumstances of underprivileged individuals.
Stabilising Prices and Taming Inflation
One of the fiscal policy’s core imperatives is inflation control and price stabilisation. Consequently, the government diligently endeavors to curtail inflation by reducing fiscal deficits, introducing tax-saving initiatives and ensuring the judicious utilisation of financial resources.
Promoting Employment
Governmental efforts to augment employment opportunities entail multifaceted fiscal measures. Infrastructure investments translate into both direct and indirect job creation. Subdued taxes and duties on small-scale industrial (SSI) units stimulate increased investment, ultimately generating more employment. Assorted rural employment initiatives, under the aegis of the Government of India, target rural challenges. Similarly, self-employment schemes are launched to provide opportunities for technically qualified individuals in urban locales.
Balanced Regional Development
Various government-backed projects, spanning dam construction, electrification, school establishments, road development, and industrial ventures, address regional imbalances. Public expenditure becomes the linchpin for mitigating regional disparities.
Balancing the Balance of Payments
Government initiatives include providing export incentives to boost outbound trade and implementing import curbs to control inbound trade. The amalgamated impact of these measures enhances the nation’s balance of payments.
Augmenting National Income
Fiscal policy yields considerable influence in achieving the desired economic outcomes. For instance, when the government seeks to augment the country’s income, it may adjust tax rates, either increasing them to raise revenue or reducing them to incentivise greater tax compliance.
Infrastructure Development
Government investments in projects like railways, schools, dams, electrification, roads, and more bolster citizens’ welfare while enhancing the nation’s infrastructure. Improved infrastructure plays a pivotal role in accelerating economic growth.
Boosting Foreign Exchange Earnings
Through incentives such as customs duty exemptions and excise duty concessions, the central government stimulates foreign investors to expand their investments within the country. This strategy bolsters foreign exchange earnings and encourages economic growth.
An expansionary economic policy stance hinges on an in-depth understanding of the implementation context and the measurement of their consequences. This process entails meticulous scrutiny of various alternatives, grounded in available data. This calls for policymakers with a diverse skill set, crucial for the effective delivery of policies to their designated beneficiaries.
That’s when the question arises, where are policymakers trained?
The Indian School Of Public Policy!
The Indian School of Public Policy (ISPP) is a testament to the collaboration of the world’s foremost policymakers, experts, and influencers. Its core mission is to revolutionise the art of policymaking, and as such, the institution is firmly grounded in its commitment to robust industry connections, a faculty of global repute, and an innovative approach to policy design and management.
The Post Graduate Programme in Public Policy, Design, and Management is ISPP’s flagship offering, tailored for individuals aspiring to drive positive global change. Spanning a year, the programme unfolds across seven terms, each lasting seven weeks, providing an immersive exploration of the intricate world of policymaking.
The PDM programme is a comprehensive journey, empowering students with a profound understanding of public policies and equipping them with the skills required to excel as adept policy analysts and executives. Over the course’s duration, students delve into the realms of public policy, finance, ethics, and the intricate workings of public administration—central areas of emphasis within this programme.
Link –https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=TOdrP-W6gmk
Register your Interest to Study at ISPP
Programme Objectives
The programme offers an in-depth exploration of the intricacies of public policy, enabling students to develop a profound comprehension of its mechanisms while imparting essential principles of design and management. Its primary aim is to cultivate a cadre of professionals and experts capable of spearheading policymaking initiatives comprehensively, emerging as adept public policy executives.
Throughout the programme, students embark on a journey of analysing policies, crafting new ones, and mastering the art of translating them into tangible real-world impact, considering factors like financial feasibility, requisite skills, and ethical imperatives. The programme is centered around examining the most effective strategies for policy implementation, proficient management, and rigorous evaluation within the realm of public administration and policymaking.
Take a peak into the class profile 2023.
Here are the highlights of the PDM programme by ISPP!
- Harris Uchicago: Certificate In Public Policy
- Immersive Learning Projects
- Interactive Labs
- Career Support & Placements
- Tea & Policy
*Programme fee may subject to change
Academic Pedagogy
ISPP adopts an all-encompassing strategy towards policy, design, and management, anchored in five core pillars: Skills (S), Political Economy (P), Ethics (E), Leadership (L), and Lifelong Learning (L). Our curriculum and learning ecosystem are meticulously crafted, and grounded in the SPELL framework, promising a comprehensive and enriching educational journey at our institution.
Here’s what life at ISPP looks like!
Student Testimonials
Our student ambassadors, composed of both alumni and current students, bring with them a wealth of expertise in public policy. They are on hand to address any queries you may have. Whether you are looking for details on our programmes, insights into the admissions process, information about campus facilities, or a glimpse into student life, our student ambassadors are at your service, ready to assist.


FAQs
What is Fiscal Policy?
Fiscal policy involves government strategies for revenue collection and spending to influence economic dynamics, especially through taxation.
What are the primary objectives of Fiscal Policy?
Fiscal policy in India aims to mobilise resources for rapid development, promote equity, stabilise prices, enhance employment, facilitate balanced regional growth, ensure a favorable balance of payments, augment national income, invest in infrastructure, and boost foreign exchange earnings.
What role does Fiscal Policy play in Infrastructure development?
Government investments in projects like railways, schools, dams, electrification, and roads enhance infrastructure, benefit citizens, and stimulate economic growth.
How does Fiscal Policy impact public finance?
Fiscal policy shapes public finances by strategically managing revenue generation, resource mobilisation, and expenditure allocation for sustainable economic development.
Where are policymakers trained?
Policymakers are trained at institutions like the Indian School of Public Policy (ISPP), which offers a Post Graduate Programme in Public Policy, Design, and Management to equip individuals with the skills needed for effective policymaking.
What is the ISPP’s approach to Policy training?
The Indian School of Public Policy (ISPP) focuses on revolutionising policymaking through faculty of global repute, robust industry connections, and an innovative approach to policy design and management.
Infographic