Table of Contents
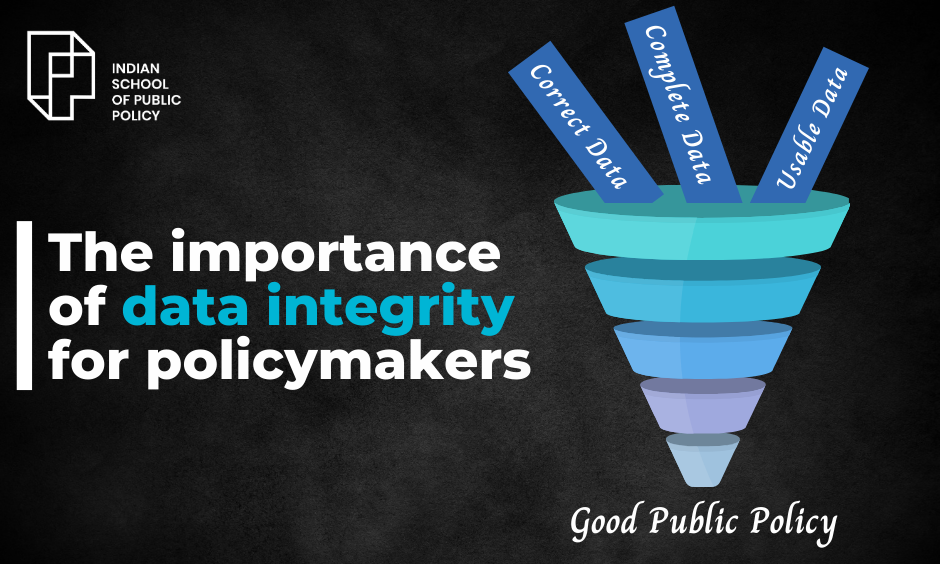
The importance of data integrity for policymakers
Why data integrity is essential for policymakers
In an age where data drives decision-making, the integrity of that data becomes paramount. For policymakers, who rely heavily on data to craft effective policies and make strategic decisions, data integrity is not just a technical concern—it is the foundation of trust and accountability. But what does data integrity entail, and why is it so critical for those shaping our societies?
What is data integrity?
At its core, data integrity refers to the accuracy, consistency, and reliability of data throughout its entire lifecycle. This means that data should be correct, complete, and usable whenever it is accessed, without having been altered or corrupted in any way. Data integrity encompasses several facets, including data accuracy, which ensures that data reflects reality; data completeness, which guarantees that all necessary data is available; and data timeliness, which confirms that data is up-to-date and relevant.
Why does data integrity matter to policymakers?
For policymakers, the consequences of compromised data integrity can be severe. Decisions based on inaccurate, outdated, or incomplete data can lead to ineffective or even harmful policies, resulting in wasted resources, misguided strategies, and a loss of public trust. Accurate data enables policymakers to understand the problems they are addressing, forecast future trends, and measure the impact of their policies.
Consider, for example, a situation where a government uses flawed health data to develop a public health strategy. If the data is not accurate—perhaps due to errors in collection, data entry mistakes, or malicious tampering—the resulting policy could fail to target the right populations or allocate resources efficiently. Such failures not only undermine the policy’s effectiveness but also erode public trust in the institutions responsible for safeguarding public welfare.
What are the consequences of poor data integrity for policymakers?
For policymakers, the repercussions of compromised data integrity can be profound and far-reaching. Decisions grounded in inaccurate, outdated, or incomplete data can lead to the development of ineffective or even harmful policies. This can result in the misallocation of resources, misguided strategic planning, and, ultimately, a failure to achieve intended policy outcomes.
Consider a scenario where policymakers rely on flawed economic data to devise fiscal policy. If the data inaccurately represents inflation rates, unemployment figures, or economic growth, the resulting policies could exacerbate economic instability, hinder growth, or disproportionately affect vulnerable populations. Such mistakes not only undermine policy effectiveness but also lead to significant financial losses and diminish public trust in government decision-making.
Moreover, poor data integrity can impact a government’s ability to respond swiftly and effectively to crises. For instance, during the COVID-19 pandemic, the integrity of health data was crucial in formulating appropriate public health responses, managing healthcare resources, and communicating transparently with the public. Inaccurate or incomplete data could lead to inadequate preparedness, delayed responses, and a higher toll on public health and safety.
For policymakers, maintaining data integrity is not just a matter of sound governance; it is vital to preserving credibility, trust, and the capacity to deliver meaningful and effective public policies.
Example: The 2018 Facebook-Cambridge Analytica Scandal
Source – https://overthinkgroup.com/facebook-cambridge-analytica/Reflecting on 2018, the Facebook-Cambridge Analytica scandal is a significant event in the history of data breaches and integrity lapses. The scandal revealed the severe consequences of mismanaging user data, raising critical concerns about privacy, accountability, and the influence of social media platforms.What happened? Cambridge Analytica, a data analytics firm, misused the personal data of 87 million Facebook users without their consent. The data was collected through a third-party app and used for political purposes, exposing the vulnerability of user information on social media. The impact Facebook’s response Key lessons learned |
The impact of data integrity on public trust
Public trust is an essential component of effective governance, and data integrity plays a crucial role in maintaining this trust. When citizens believe that their government is transparent, competent, and uses reliable data to make decisions, they are more likely to support those decisions, comply with regulations, and participate in democratic processes.
Conversely, when data integrity is compromised, trust is quickly eroded. For example, if there are reports of data manipulation or inaccuracies in crime statistics, the public may lose confidence in the government’s ability to ensure safety and justice. Transparency in data collection and validation processes, therefore, becomes essential. Governments must demonstrate their commitment to maintaining data integrity by being open about their data sources, methodologies, and any limitations that may affect the data’s reliability.
What is the role of data governance and regulation?
Ensuring data integrity is not solely the responsibility of data scientists or IT professionals. Policymakers themselves have a critical role in fostering an environment where data integrity is prioritised. This involves establishing clear data governance frameworks that define how data should be collected, stored, processed, and shared.
International standards and regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union, promote best practices for data protection and integrity. Adopting such frameworks can help governments ensure that their data remains reliable and secure, thereby supporting sound decision-making and policy formulation.
What are some technological solutions to enhance data integrity?
Technology offers powerful tools for maintaining data integrity. For example, blockchain technology can create immutable records, reducing the risk of tampering or fraud. Artificial intelligence (AI) can detect anomalies and patterns in large datasets that may indicate errors or data corruption. Meanwhile, data encryption can protect sensitive information from unauthorised access or breaches.
Governments and organisations worldwide are already leveraging these technologies to enhance data security and integrity. For instance, some countries have adopted blockchain to maintain transparent and secure records of land ownership or public expenditure. Such initiatives not only safeguard data but also build public trust by ensuring that data is accurate, accessible, and verifiable.
What are some recommendations for policymakers and aspirants?
Data integrity is more than a technical issue; it is the bedrock of effective policy making and public trust. In an increasingly data-driven world, maintaining data accuracy, consistency, and reliability is essential for crafting sound policies that serve the public good. As stewards of public data, policymakers must be vigilant, proactive, and committed to upholding the highest standards of data integrity to ensure that their decisions are informed, fair, and effective.
Policymakers can take the following several steps to prioritise data integrity.
Firstly, investing in robust data management infrastructure is crucial. This includes not only technology but also skilled personnel trained in data science, data governance, and ethical data handling.
Secondly, establishing clear data governance policies and frameworks can help ensure that data is collected, processed, and stored consistently and transparently. Regular audits and data validation processes can further enhance data integrity by identifying and correcting errors or discrepancies early on.
Fostering a culture of transparency and accountability in data management is key. Policymakers should be proactive in communicating how data is collected, validated, and used in decision-making processes, thereby enhancing public confidence in the data that underpins policy decisions.
Policymakers can also protect themselves and enhance their capacity to handle data effectively by pursuing formal education in public policy. Programmes such as a Postgraduate Programme in Public Policy, Design, and Management offered by top institutes in India provide essential skills in data analysis, governance, and ethical decision-making.
What are some reasons for you to opt for the Post Graduate Programme in Public Policy, Design, and Management by ISPP?
The programme provides an in-depth exploration of Public Policy and its development processes, furnishing students with key principles in design and management. It aims to cultivate skilled systems thinkers and effective policy leaders.
- Harris UChicago: Credential in Public Policy
- Engaging Learning Experience
- Hands-On Interactive Labs
- Tea & Policy
Register your Interest to Study at ISPP
Infographics: